Suncreen, why use it?
Written by Jeffrey Davis on July 8, 2011, 1:36 a.m.
First, lets cover the basics of sun exposure and why sunscreen is important.
Melanoma.
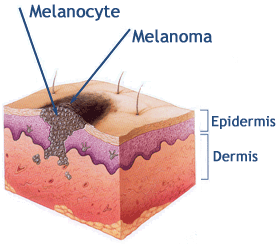 This cancer is on the rise and almost 70% of cases worldwide may be attributed to excess sun exposure. UV radiation is the specific type of light that is implicated and is made up of both UV-A and UV-B. Fair skinned people are 20 times more likely to get melanoma than blacks. Multiple studies have linked tanning bed usage to an increased incidence of melanoma.
This cancer is on the rise and almost 70% of cases worldwide may be attributed to excess sun exposure. UV radiation is the specific type of light that is implicated and is made up of both UV-A and UV-B. Fair skinned people are 20 times more likely to get melanoma than blacks. Multiple studies have linked tanning bed usage to an increased incidence of melanoma.
Skin Damage
 Long term exposure to the sun leads to wrinkling and decrease collagen and elastin (the stuff that makes skin tighter). Both lead to premature aging of the skin.
Long term exposure to the sun leads to wrinkling and decrease collagen and elastin (the stuff that makes skin tighter). Both lead to premature aging of the skin.
The Basics of Sun Protection
These are the guidelines put forth by the National Council on Skin Cancer Prevention:
- Do NOT burn. Avoid sun tanning and tanning beds, consider a self-tanning product and continue to use sunscreen
- Generously apply sunscreen to all exposed skin using at least SPF 15 and which provides both UVA and UVB protection. Re-apply every two hours even on cloudy days.
- Wear protective clothing (long sleeves, pants, wide brimmed hat and sunglasses
- Seek shade between the hours of 10am and 4pm
- Use extra caution near water, sand or snow as the sun's rays are reflected
- Get vitamin D through a healthy diet that includes vitamin supplements
SPF
Most people using sunscreen are not applying enough of the product. Most adults should be using 1-2 oz of product to cover exposed skin. In studies, adults were only applying enough sunscreen to achieve one third to one half its rated SPF.

SPF rating will change in the summer of 2012 but some manufacturers will change their labeling before this. What's prompted this change? When SPF was introduced it was designed to give people information in preventing sunburns (caused by UVB) and did not address protection from UVA (also linked to melanoma). The new rule will require manufacturers that label their product as broad spectrum to offer at least SPF 15 against both UV A & B. They also will not be able to label them as sweat-proof or waterproof and will require instructions to re-apply every two hours.
I recommend choosing a sunscreen that is between SPF 30 and 50 (there is no evidence that anything above 50 is better) and provides broad spectrum protection. If you will be sweating or participating in water activities choose one that is water resistant (the new label will specify if reapplication is needed at 40 min or 80 min). I also recommend using a sunscreen with micronized zinc or titanium. Avoid chemicals such as retinyl palmitate (linked to skin cancer in animals), parabens (a frequent cause of allergic reactions and dermatitis), and phthalates (which act as anti-androgens and cause reproductive problems).